The Westinghouse 19B (X19B) was a production development of the X19A.
Change in design include externally mounted accessories for better accessibility, a new type burner chamber and various other minor improvements.

Westinghouse 19B
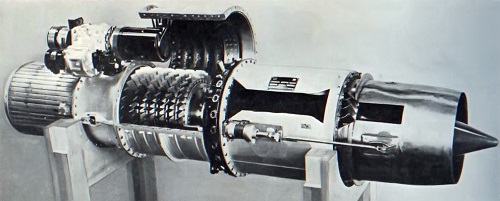
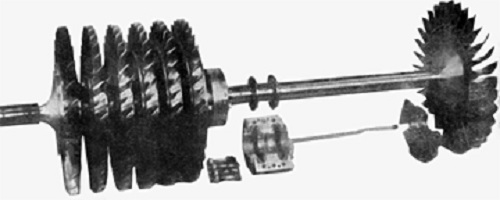
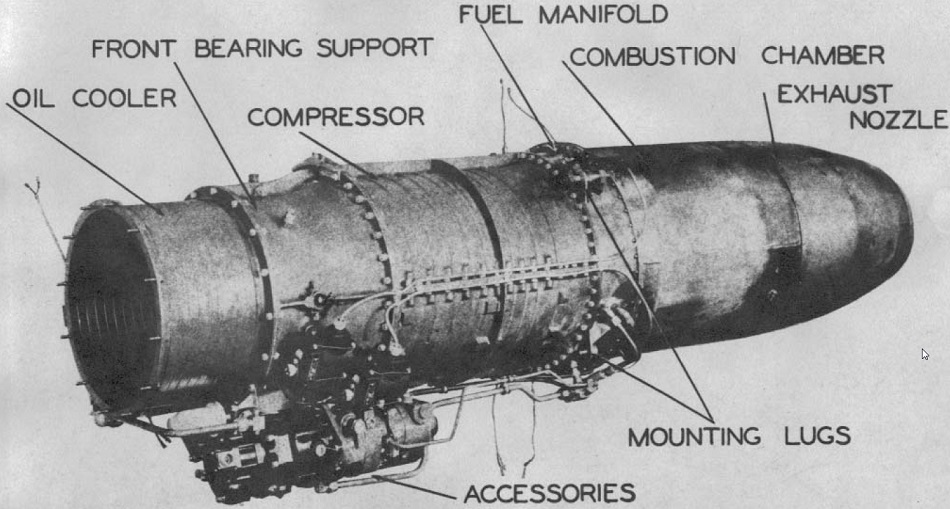
The 19B was to have a static thrust of 613 Kg (1350 lb) and be used as the main propulsion engine for an aircraft, rather than just a booster. The layout of the compressor and turbine was similar to the 19A. The oombustion chamber is an annulus in which is mounted an annular combustion basket containing holes that meter the charge air to the primary and secoe burning zones, Fuel is supplied to the oambustion chamber through 24 fuel nozzles oircumferentially mounted in a manifold at the forward end of the chamber.
First flight was made on 28 september 1944, using a JM-1 Marauder as a test-bed.
The McDonnell XFD-1 Phamtom powered by two 19Bs made its first flight on january 26, 1945. The Northrop XP-79B was also powered by two 19Bs, but crashed on its first flight on september 12, 1945.
A total of 28 19B were ordered.

Westinghouse 19XB (J30)
Westinghouse submitted to the Navy a proposal for improving the performance and decreasing the weight of the 19B. This reconfigured engine was designated 19XB. The 1,600 lb thrust of the 19XB was achieved primarily by adding 4 additionnal axial-flow compressor stages.
The 19XB was used in the Gruman WTB3F-1, Douglas XB-42A (as auxiliary engines) and the Northrop X-4. The primary application for the 19XB engine was the McDonnell FH-1 Phantom.
A total of 261 19XB engines were made.
Notes et Références
Westinghouse 19A
Design of 19A Yankee was begun on 10 August 1942. It had six axial stage compressor, a twenty four cannular combustion chamber and a single stage turbine.
On 19 March 1943, the first run was made. The static thrust developped being 515 kg (1,135 lb). On 21 January 1944 the second prototype was flown for the first time, using a Vought FG-1 Corsair.
Six 19A were built all together.

